Worms in horses may be tiny, but their impact on a horse’s health can be monumental. If left untreated, these unwanted guests can lead to several health issues related to digestion, weight, or long-term damage to internal organs. This makes deworming in horses not just smart but a necessity to support ideal health.
That said, figuring out the timing and deworming schedules can feel overwhelming. From changing seasons to various factors and tests, there are so many things to consider. If you find yourself in the same vein, don’t worry.
This informative blog will cover everything about deworming in horses. You’ll learn about the frequency of deworming in horses and foals during the various seasons and how schedules are formulated. Furthermore, we’ve covered some of the most trusted worming treatments and valuable preventive measures to ensure comprehensive protection against equine parasites.
Ready with your notepads? Let’s go!
How Often Should Horses Be Dewormed?
The correct answer to this question depends on various factors, including the horse’s age, health, lifestyle, geographical location, and fecal egg count. Therefore, to recommend a personalized deworming schedule, the vet will suggest a fecal test. This test helps determine the number of parasitic eggs per gram of manure.
Here’s what you need to keep in mind while collecting a fecal sample:
- Collect the sample and keep it in an airtight Ziploc bag or container.
- Fresh samples (less than 12 hours old) are best for fecal examination.
- It’s best to refrigerate the sample as soon as you collect it.
- The sample should be tested within 7 days of collection.
- For egg count, the fecal sample of a horse suffering from diarrhea is not suitable.
- Also, the sample should not be frozen, as it may affect the egg count.
Depending on the fecal examination, the horse will be classified as a low, moderate, or high shedder (EPG), and a suitable deworming schedule can be formed.
The following table will give you a general idea of deworming in horses. However, you should always consult a veterinarian for tailored deworming recommendations:
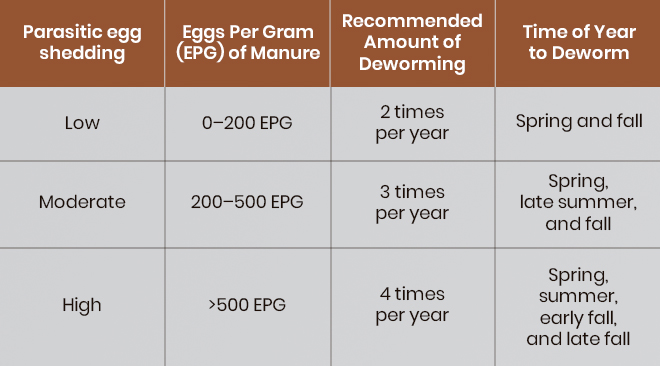
Seasonal Deworming Schedule for Adult Horses
In this segment, we’ll understand the seasonal schedules for the deworming of adult horses. These schedules are presented as per the parasite egg shedding rate in different seasons, along with the best-suited deworming treatment options.
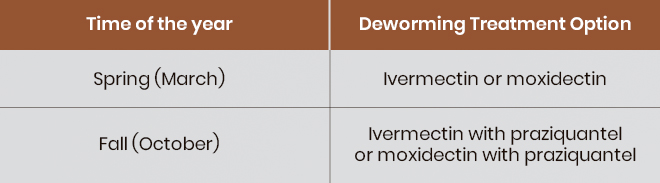
Low Shedder (0–200 Eggs Per Gram of Manure):
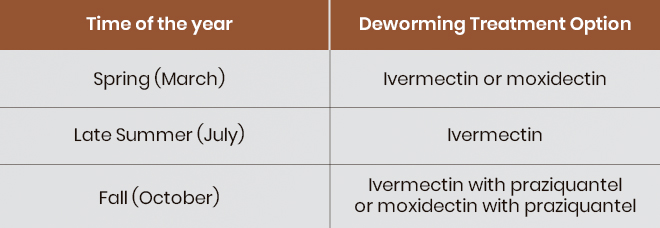
Moderate Shedder (200–500 Eggs Per Gram of Manure):
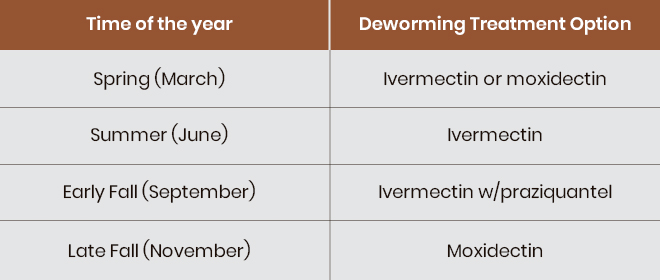
High Shedders (>500 Eggs Per Gram of Manure):
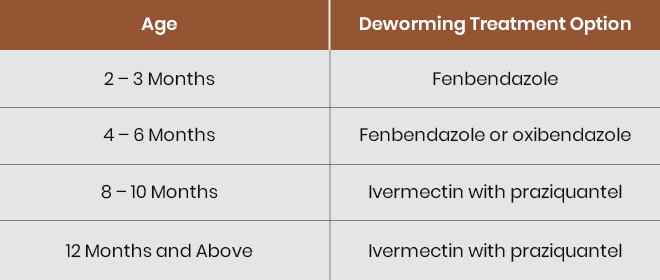
Deworming Schedule for Foals
Foals and young horses are especially vulnerable to parasites due to their weak or developing immune systems and require frequent deworming. Here’s a deworming schedule to give you a general idea:
Popular Deworming Treatments for Horses
These are some of the popular deworming treatments for horses you can look into to ensure your horse’s protection.
Panacur Equine Granules: Panacur Equine Granules is a potent oral wormer, formulated to protect horses against a range of intestinal worms. With Fenbendazole as the active ingredient, this treatment treats and controls roundworms, as well as large strongyles, and adult and immature small strongyles. It also has an ovicidal effect on nematode eggs.
Equimec Plus Tape: Equimec Plus Tape is a broad-spectrum wormer formulated with ivermectin and praziquantel to protect horses against a wide range of parasites. This oral treatment treats and controls roundworms (including arterial larval stages of Strongylus vulgaris and benzimidazole-resistant small strongyles), tapeworms, bots and skin lesions (summer sores) caused by Habronema and Draschia spp. and Onchocerca spp. (cutaneous onchocerciasis).
It also offers protection against tapeworms, pinworms, bots, ascarids, lungworms, hairworms, neck threadworms, large-mouth stomach worms, and intestinal threadworms. Furthermore, it effectively controls skin lesions caused by Habronema, Draschia, and Onchocerca species.
Eraquell Oral Paste: This broad-spectrum oral paste wormer contains ivermectin as the active ingredient to protect against various internal parasites. The Eraquell oral paste treats and controls large strongyles (bloodworms) (Strongylus spp., Triodontophorus spp.), small strongyles (redworms) (Cyathostomum spp.) Including benzimidazole (BZ) resistant strains, pinworms (Oxyuris equi), large roundworms (Parascaris equorum), hairworms (Trichostrongylus axei), intestinal threadworms (Strongyloides westeri), bots (Gasterophilus spp.) and lungworm (Dictyocaulus arnfieldi).
Measures to Prevent Worms in Horses
Here are some practical measures you can take to keep your horses protected against the dread of worms:
- Schedule regular vet visits and take follow-ups seriously.
- Administer the vet-recommended wormer as per the schedule provided by the vet.
- Regularly remove feces from the grazing pastures.
- Do not overstock pastures.
- Periodically rotate pastures with other grazers to interrupt the lifecycle of equine parasites.
- Quarantine the new horses for some days before adding them to the main herd.
Parting Words
We hope this guide helped you feel that deworming in horses is not as daunting as it sounds. With the right knowledge, you can take timely measures and stay ahead of these pesky parasites. Remember to follow the preventive measures to ensure your horse’s safety from the invisible threat of parasites.
For any doubt, it’s best to consult your vet. They will provide personalized guidance after considering your horse’s health condition and medical history.


